Cervical Cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. Cancer is always named for the part of the body where it starts, even if it spreads to other body parts later. When cancer starts in the cervix, it is called cervical cancer.
The cervix connects the vagina (birth canal) to the upper part of the uterus. The uterus (or womb) is where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant.
All women are at risk for cervical cancer. It occurs most often in women over age 30. Long-lasting infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer.
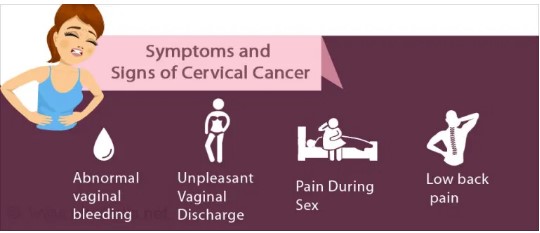
Symptoms :
Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between periods or after menopause
Watery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and have a foul odor
Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse
Causes :
Cervical cancer begins when healthy cells in the cervix develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do.
Healthy cells grow and multiply at a set rate, eventually dying at a set time. The mutations tell the cells to grow and multiply out of control, and they don’t die. The accumulating abnormal cells form a mass (tumor).
Cancer cells invade nearby tissues and can break off from a tumor to spread (metastasize) elsewhere in the body
